rotator cuff tests drop arm|positive drop arm sign : wholesalers The test is positive when weakness or pain causes them to drop the arm to their side. most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus Resultado da Cidade: Tanabi-SP Data Falecimento: 03/02/2024 Data Sepultamento: 04/02/2024 Hora Sepultamento: 10:00 Hrs. ROBERTO APARECIDO MORATO. 64 Anos . “Obrigado a Funerária Central pelo atendimento e atenção deste momento de sofrimento em que perdemos esse menino tão .
{plog:ftitle_list}
14 de fev. de 2022 · MEGA是一个用于多序列比对和可视化、以及构建系统发育树的免费程序。自1993年发布以来,MEGA共更新 9个版本 (没有第八、九版),今年发布的MEGA 11为处理更大的数据集进行了优化。 之前我们介绍的DNAMAN和Jalview (.
shoulder test for rotator cuff
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers.The Diagnostic Accuracy of Special Tests for Rotator Cuff Tear: The ROW Cohort Study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;96(3):176-183.
A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11).
instron tensile compression tester model 4481
This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included. The test is positive when weakness or pain causes them to drop the arm to their side. most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus How it’s performed: A doctor will raise your arm to your side and bend your elbow to 90 degrees. You will then externally rotate your arm as the doctor resists. What it tests for: Damage to the. The drop arm test can help determine the integrity of the rotator cuff musculature, specifically supraspinatus. A positive test is the inability of the individual to lower their arm to their side under control from 90 degrees of .
Drop Arm Sign for Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears. The Drop Arm Sign has a sensitivity of 73% and a specificity of 77% in the diagnosis of full-thickness tears of the Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus tendons according to a study done by . This is a really great test for you to use with your patients who you suspect may have injured their Rotator Cuff, and in particular, may have suffered a Rot.
Drop Arm Sign for Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears. The Drop Arm Sign has a sensitivity of 73% and a specificity of 77% in the diagnosis of full-thickness tears of the Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus tendons according to a study done by . Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. . Drop arm .
The aim was to assess diagnostic accuracy of 15 shoulder special tests for rotator cuff tears. From 02/2011 to 12/2012, 208 participants with shoulder pain were recruited in a cohort study. . bear hug, external rotation lag sign at 0°, external rotation lag sign at 90°, Hornblower’s sign, full can test, drop arm test, Jobe’s test, Neer .Jobe’s test; Drop arm test; Neer test; Test for Teres minor: Hornblower’s Sign; To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed. A cluster improves the post-test probability for the clinical diagnosis of a full-thickness tear. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles in the shoulder that allow a wide range of movement while maintaining the stability of the glenohumeral joint (see Image. . Painful arc test, drop arm test, and weakness in the external rotation is the most common observations on physical examination.The cluster for a full thickness rotator cuff tear includes 1. the Drop-arm sign, 2. the painful arc sign, and 3. infraspinatus manual muscle test. If all three tests are positive, the +LR is 15.6 . (Note is 3/3 are positive and the patient is greater than 60 years old the +LR increases to 28)
Two such commonly employed shoulder tests to diagnose a torn rotator cuff is the Drop Arm Test and the Hornblower Test. More than pain in the shoulder joint, it is significant weakness on the affected side that could be a strong indicator of rotator cuff tears. Along with these tests imaging tests like an MRI could help confirm the diagnosis.This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests .
Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis. . The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that hold the shoulder joint in place and allow you to move your arm and shoulder. Problems with the .
A rotator cuff tear is an injury to your rotator cuff that can cause shoulder pain and the inability to use your arm. Your rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons in your shoulder. They help you lift and move your arms away from your body. Your rotator cuff keeps the ball of your upper arm bone in the shoulder blade socket.
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as: This tests the Supraspinatus tendon. Drop Arm Test (Codman’s Test) Your arm will be moved above your head, and you’re asked to gently lower your arm to your side. If you can’t do this slowly and under control or have severe pain in doing so, it suggests a tear in the rotator cuff, specifically Supraspinatus. Abrasion Sign. You will be . Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B. Drop arm test. The drop arm test is used to assess for rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. Interpretation. Drop arm test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and .
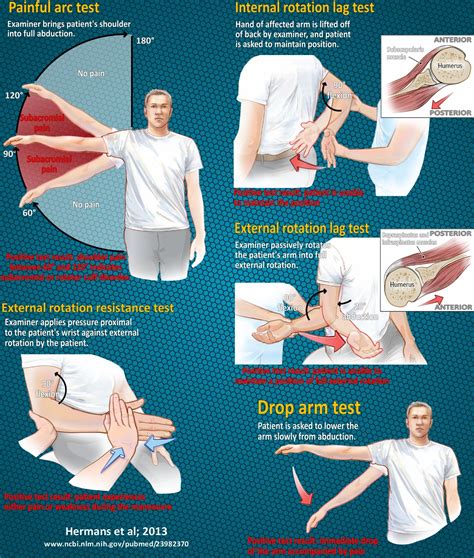
Rotator Cuff. Supraspinatus (SS) Jobe’s test: Positive test is pain/weakness with resisted downward pressure while the patient’s shoulder is at 90 degrees of forward flexion and abduction in the scapular plane with the thumb pointing toward the floor. Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of . The following factors may increase the risk of having a rotator cuff injury: Age. The risk of a rotator cuff injury increases with age. Rotator cuff tears are most common in people older than 60. Some occupations. Jobs that require repetitive overhead arm motions, such as carpentry or house painting, can damage the rotator cuff over time . Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner.
Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign. Technique [edit | edit source] The therapist passively raises the patient's arm to 90 degrees of abduction. The patient then lowers the arm back to neutral with the palm down. - Drop arm test - External rotation testing of shoulder - Passive Painful Arc Neer Test - Scapular assistance maneuver . - Painful arc sign for rotator cuff pathology - Jobe test of supraspinatus strength - External rotation test - Gerbers test - .
If the arm drops or shrugs, then the rotator cuff likely isn’t able to counterbalance the superior line of pull of the deltoid. The research has shown that the sensitivity of the drop arm test is low to moderate, but specificity is high from 80-100%. Your rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that connects your shoulder blade to your upper arm bone (humerus).You use your rotator cuff to raise your arm overhead and to rotate your arm toward and away from your body. The rotator cuff sits in a small space between your humerus and the acromion (the upper part of your shoulder blade).
Sensitivity & Specificity. A literature review 1 in MEDLINE was performed for physical examination tests/maneuvers of the rotator cuff tears, and found that drop arm sign has the following accuracy:. Sensitivity: 73 %; Specificity: 98 %; Another study by Walch G 2 found that this test has a 100% sensitivity and a 100% specificity for irreparable degeneration .Rotator Cuff Tests. Supraspinatus Test (+ LR 3.2) Abduct arm to 90', forward flex it 30' with thumb down ("empty beer can position") . Drop arm test Patient is unable to hold or smoothly lower an extended arm at 90' of shoulder abduction with out dropping it; Differential Diagnosis
The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. To perform the Drop Arm test, position the patient in sitting or standing with the arm relaxed at their side. The examiner passively places the patient’s arm into abduction of .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). This test can also be used for the clinical examination of a shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS).. Another name for this test is the Infraspinatus .This review aimed to compare the diagnostic accuracy of commonly used clinical tests for posterosuperior rotator cuff tears. . 6 tests were eligible for meta-analysis: drop arm sign, Jobe test, external rotation lag sign, Hawkins-Kennedy test, Neer test and painful arc abduction test. According to QUADAS-2 criteria, risk of bias was low in 1 .
instron tensile compression tester model 4481 diagrams
WEBHTTP 409 状态码. 409 Conflict. 由于和被请求的资源的当前状态之间存在冲突,请求无法完成。. 这个代码只允许用在这样的情况下才能被使用:用户被认为能够解决冲突,并且会重新提交新的请求。. 该响应应当包含足够的信息以便用户发现冲突的源头。. 冲突通常 .
rotator cuff tests drop arm|positive drop arm sign